Modeling Structure in Revit®: 3. Practical guidelines for modeling vertical structural elements
Practical guidelines for modeling structural elements in Revit® include:
Guidelines for vertical structural elements:
- Modeling structural bearing walls
- Modeling structural non-bearing walls
- Modeling other (non-structural) walls (in case they are needed for some reason).
- Modeling structural columns
guidelines for horizontal structural elements:
- Modeling structural floors
- Modeling structural framing
- Modeling structural foundations
General rule is to model everything the same way as it’s going to be built. There are some exceptions, for example, cast in-place walls, columns and beams are modeled to the top of slabs, but with use of Revit® Join Geometry tool we get it right in the end (as it will be “poured”). (edited 2019-11-10) This workflow is revised below since material quantities and pour breaks depend on correct division of the model and should not be dependent on regardless of joined or not joined geometry. Final product must be appropriate for drawings production, further IFC and other file exports, scheduling / material takeoffs, and structural (analytical) analysis uses.
General Revit® template settings
Before we start modeling structural elements, we need to make sure that we set up our structural Revit® template right and, more important, that our levels and grids are set according to guidelines for levels and grids in structural model.
Let’s look back and repeat what kinds of Level Types are used:
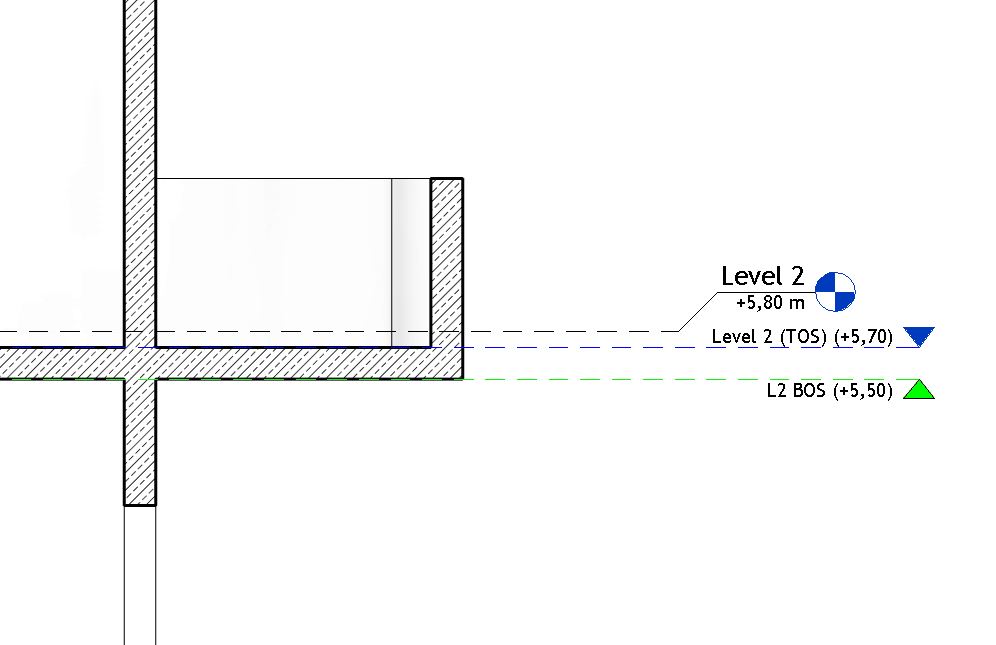
Level 1 type is FF (Finished Floor), it’s used just for coordination purposes with architectural and other disciplines.
Level 1 (TOS) type is TOS (Top of Structure), most of the structure is referenced to this kind of level (has Building Story parameter set to true, has Structural parameter set to true)
L1 BOS type is BOS (Bottom of Structure), used for special elements in structure that need to be referenced to the bottom of slab or similar.
Vertical structural elements
Modeling structural bearing walls
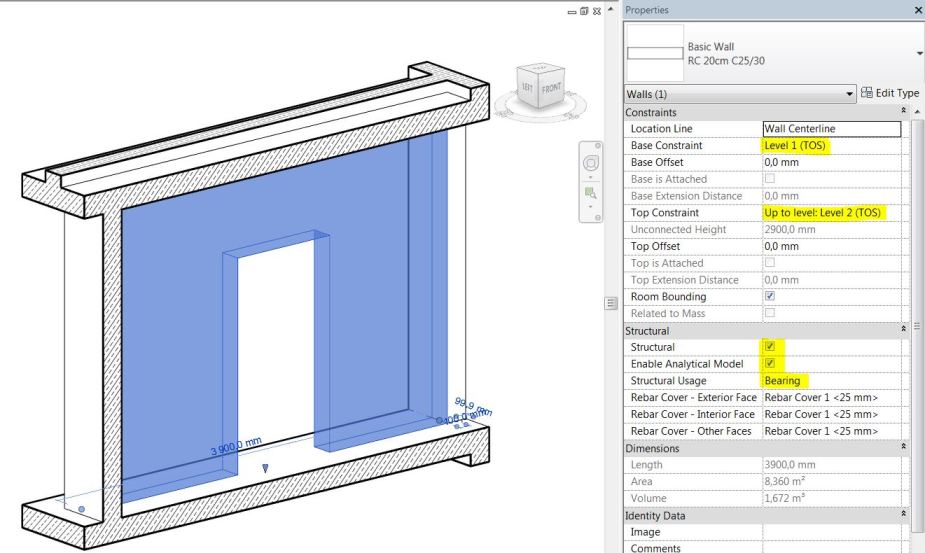
- Structural bearing walls are modeled from TOS level to the BOS level above.
- Bearing walls have instance parameter Structural set to true (checked).
- Enable Analytical Model property is set to true if the model element is used for structural analysis.
- Avoid attaching top or bottom walls to floors or roofs. Instead, use Join Geometry option. Attach only when floor or roof are not horizontal. Other solution is to use Edit Profile feature.
- For analytical purposes and visual fidelity, make sure material and layered structure settings are set correctly. Quick check of all layered structures can be easily done with our free Revit® add-in Engipedia Layers Manager.
Modeling structural non-bearing walls
Structural non-bearing walls are those that are not used in load bearing system but impose significant loads to the structure, or those that are added later as integral part of a structure (masonry walls for example).
- Non-bearing walls are modeled from TOS level to the BOS level above.
- Non-bearing walls have instance parameter Structural set to false (unchecked).
- Enable Analytical Model property is set to false.
- Avoid attaching top or bottom walls to floors or roofs. Instead, use Join Geometry option. Attach only when floor or roof are not horizontal. Other solution is to use Edit Profile feature.
- For visual fidelity, make sure material and layered structure settings are set correctly.
Modeling other (non-structural) walls
Other non-bearing walls are for example interior drywall or other room separation walls that we might want to have inside our structural Revit® model (from whatever reason).
- Other non-bearing walls are modeled the same way they are going to be build, meaning they can be referenced from FF level (with negative bottom offset for example) to the BOS level above.
- Non-bearing walls have instance parameter Structural set to false (unchecked).
- Enable Analytical Model property is set to false.
- Avoid attaching top or bottom walls to floors or roofs. Instead, use Join Geometry option. Attach only when floor or roof are not horizontal. Other solution is to use Edit Profile feature.
- For visual fidelity, make sure material and layered structure settings are set correctly.
Modeling structural columns
Structural columns are modeled the same way as load bearing structural walls.
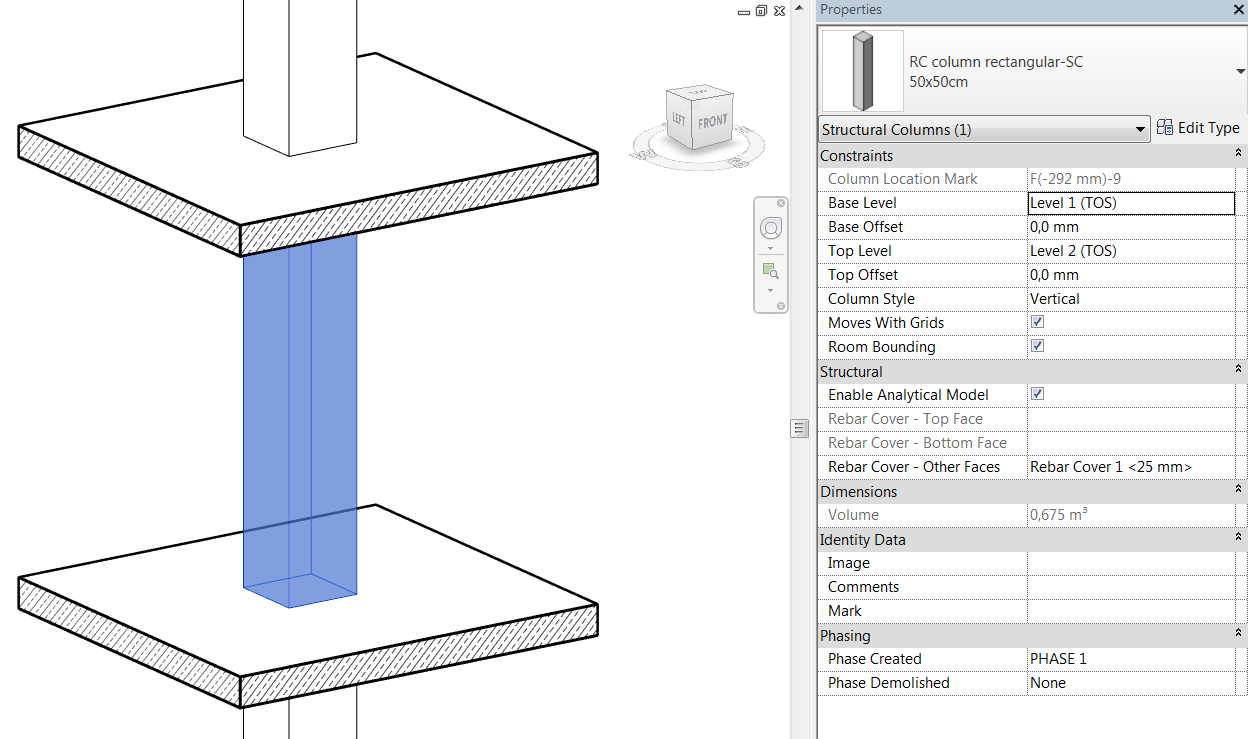
- Structural columns are modeled from TOS level to the BOS level above.
- Enable Analytical Model property is set to true if the model element is used for structural analysis.
- Avoid attaching top or bottom of columns to floors or roofs. Instead, use Join Geometry option. Attach only when floor or roof are not horizontal.
- For analytical purposes make sure to use built-in Structural Material parameter.
- For visual fidelity make sure material settings are set correctly, also make sure to use appropriate (custom) Sub-category (if there aren’t any, create Concrete, Steel, Timber as sub-categories in Structural Columns category family).
